Switzerland Road extraction from historical maps: Difference between revisions
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
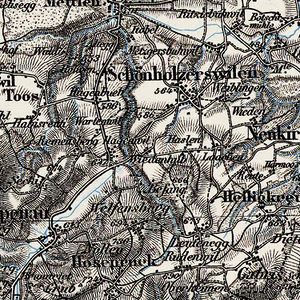
*'''Dataset''': Dufour Map from GeoVITE (The 1:100 000 Topographic Map of Switzerland was the first official series of maps that encompassed the whole of Switzerland. It was published in the period from 1845 to 1865 and thus coincides with the creation of the modern Swiss Confederation.) | *'''Dataset''': Dufour Map from GeoVITE (The 1:100 000 Topographic Map of Switzerland was the first official series of maps that encompassed the whole of Switzerland. It was published in the period from 1845 to 1865 and thus coincides with the creation of the modern Swiss Confederation.) | ||
(1)Classification : Main roads | |||
(2)Layer: Topographic Raster Maps------Historical Maps------Dufour Maps | (2)Layer: Topographic Raster Maps------Historical Maps------Dufour Maps | ||
| Line 71: | Line 69: | ||
(5)Patch Size: 1000 * 1000 | (5)Patch Size: 1000 * 1000 | ||
*'''dhSegment''': a generic framework for historical document processing using Deep learning approach, created by Benoit Seguin and Sofia Ares Oliveira at DHLAB, EPFL. | |||
*'''Data paraparation''' | *'''Data paraparation''' | ||
Revision as of 19:24, 24 November 2021
Introduction
Historical maps provide valuable information about spatial transformation of the landscape over time spans. This project, based on historical maps of Switzerland, is to vectorize road network and landcover and to visualize the transformation using a machine vision library developed at the DHLAB.
The main data source of this project is GeoVITe (Geodata Versatile Information Transfer environment),a browser-based access to geodata for research and teaching, operated by the Institute of Cartography and Geoinformation of ETH Zurich (IKG) since 2008.
Motivation
Historical maps contain rich information, which are helpful in urban planning, historical study, and various humanities research. Digitization of massive printed documents is a significant step before further research. However, most historical maps are scanned in rasterized graphical images. To conveniently use geographic data extracted from these maps in GIS software, vectorization is needed.
However, vectorization process has always been a challenge due to manual painting. In this project, we try to use dh-segmentation tool for automatic vectorization. With 60 high-resolution patches(1km*1km) for the training dataset, the model is tested on randomly selected patches and proposed to approximate idealized main roads of Dufour map of Switzerland.
Plan and Milestones
| Date | Task | Completion |
|---|---|---|
| By Week 4 |
|
✓ |
| By Week 6 |
|
✓ |
| By Week 8 |
|
✓ |
| By Week 10 |
|
... |
| By Week 12 |
|
... |
| By Week 14 |
|
... |
Methodology
- Dataset: Dufour Map from GeoVITE (The 1:100 000 Topographic Map of Switzerland was the first official series of maps that encompassed the whole of Switzerland. It was published in the period from 1845 to 1865 and thus coincides with the creation of the modern Swiss Confederation.)
(1)Classification : Main roads
(2)Layer: Topographic Raster Maps------Historical Maps------Dufour Maps
(3)Coordinate system: CH1903/LV03
(4)Predefined Grids: 1:25000
(5)Patch Size: 1000 * 1000
- dhSegment: a generic framework for historical document processing using Deep learning approach, created by Benoit Seguin and Sofia Ares Oliveira at DHLAB, EPFL.
- Data paraparation
geovite (get url, downloading directly for small patches) map.geo.admin.ch (swisstopo): only black-and-white images -> difficult to annotate with low resolution
- Labeling
60 patches (1000x1000 pixels) using Gimp for model testing: original tiff patches, original images with jpeg format, labels(masks) with png format (white main roads and black background)
Limitation
The main limitation of our project is due to the data source platform. GeoVITE only allows small patches downloading, while automatic downloading leads to unsatisfying low-quality images.