3DVeniceWellheads: Difference between revisions
Loic.rochat (talk | contribs) |
Loic.rochat (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
| | | | ||
* Midterm presentation | * Midterm presentation | ||
* Design a Grasshopper model to extract parameters from pictures and output a JSON file. | * Design a Grasshopper model to extract parameters from pictures and output a JSON file. | ||
* Scan the book ''Vere Da Pozzo'' | |||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
|By Week 11 | |By Week 11 | ||
| | | | ||
* Definitive 3D model | * Definitive 3D model on Grasshopper. | ||
* Wells parametrization and 3D reconstruction | * Wells parametrization and 3D reconstruction | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | | ||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
|By Week 12 | |By Week 12 | ||
| | | | ||
* Create a JSON file with well-head ID, location coordinates, link to the 3D model, the square name, the construction time, the material and the height. | |||
* Provide either the images of the well-heads through a unique PDF or as a set of individual files. | |||
* Wells parametrization and 3D reconstruction | * Wells parametrization and 3D reconstruction | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | | ||
| Line 100: | Line 102: | ||
|By Week 13 | |By Week 13 | ||
| | | | ||
* | * Preparation for the final presentation | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 12:29, 21 November 2021
Introduction
Hello this is the intro
Book Vere Da Pozzo Di Venezia, Alberto Rizzi, La Stamperia Di Venezia Editrice, 1981.
search for images of wells
Motivation
Venice is one of the cities in Europe with the richest and largest number of well-heads, locally known as "vere da pozzo". This term refers to the stone structure surrounding the pipe of a well with protective function. Across history, the role of wells for Venice has always been crucial, in first place to assure drinking water for citizens. Although on water, the city needed wells to store unsalted water. They were placed most of the times in the middle of a square or a private courtyard to collect rainwater and filter it in the ground. In times of drought they were filled with freshwater from the near Brenta river. Over time the uncovered part of these wells, the visible one, started to become more and more relevant also in cultural and artisitc terms. The aim of the project is thus to highlight their significance by classification and 3D modelling. With such an augmentation, we could expect to be able to extract information about their common structures and patterns and also their positioning.
Project Plan
Main steps of the project:
- Preliminary research on the net and books: wells classification.
- Identification of common and particular features.
- Definition of parameters to describe all these traits digitally.
- Creation of one single 3D model capable of describing the larger number of possible wells.
- Starting from this model, replica of the wells in the book "Vere da Pozzo di Venezia" by Alberto Rizzi.
- Wells database (?).
- Wells placing (?).
- Tada!
| Date | Task | Completion |
|---|---|---|
| By Week 3 |
|
✓ |
| By Week 4 |
|
✓ |
| By Week 5 |
|
✓ |
| By Week 6 |
|
✓ |
| By Week 7 |
|
✓ |
| By Week 8 |
|
|
| By Week 9 |
|
|
| By Week 10 |
|
|
| By Week 11 |
|
|
| By Week 12 |
|
|
| By Week 13 |
|
|
| By Week 14 |
|
Methodology
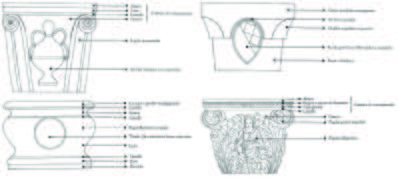
The well-heads of Venice or "vere da pozzo" feature detailed artworks such as stone sculptures. It is challenging to replicate them with a procedural 3D modelling process. The goal is to identify the most basic typologies of wells with basic geometric shapes and use them to model a simple shape of each well with Rhino Grasshopper.
Common typologies of wells:
- Base with circular, square, hexagonal, octagonal, decagonal (10), dodecagonal (12) shapes.
- Top with circular, square, hexagonal, octagonal, decagonal (10), dodecagonal (12) shapes.
- Edges are either sharp or embedding a sculpture that cut them.
- Well-heads rest on a slab with one, two or three steps.
- Top 10-15cm of the well either have flanges with square or circular profiles or arcades
The following illustrations come from the book Vere Da Pozzo Di Venezia, Alberto Rizzi, La Stamperia Di Venezia Editrice, 1981. They illustrate the typologies.
Classification by stylistic appearance and historical period:
| Type | Period | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Archeological | Greek and Roman | Rough, made from column shafts, altars, memorial stones, cinerary urns and other pieces. |
| Carolingian | VIII-X centuries | Cubic, decorated with symbols of Christian art |
| Venetian-Byzantine | XI-XIII centuries | Free-standing cylinder decorated with pillars or columns |
| Gothic | XIV-XV centuries | Like capitals of columns or pillars, with square frame |
| Traditional | from 1300 | Cylindrical shaft with small arches in the corners |
| Lombardesque | late XV-early XVI centuries | Modelled like columns capitals |
| Renaissance | mid XV-mid XVI centuries | Polygonal shape with figures in the lateral boxes |
| Baroques | XVI-XVIII centuries | Double swelling in the middle |
| Neoclassical | XVIII-XIX centuries | Very simple cylindrical structure |
Set of parameters:
- Number of slabs
For each slab:
- Height
- Outer diameter (without mouldings)
- Number of polygonal edges at the top, 0 for circle
- Number of polygonal edges at the bottom, 0 for circle
For the outline of the moulding:
- Starting point position and direction (2D)
- Ending point position and direction (2D)
- Middle point position, direction (2D) and scale factor of the opposite direction
- Shear factor
Results
Future work
- scan a sample of representative wells, perspectives : 1h
- design a grasshopper code to generate json out of the images: 5h
- scan the book as PDF or as a set of JPG: 5h
- generate the JSONs: 16h
- classify the well-heads of the book ?h