Widows in Venice
Introduction
Widows in historical societies often occupied a unique socio-economic position, navigating the dual challenges of loss and the constraints of societal structures. This project seeks to explore the socio-economic status and property dynamics of widows as recorded in two historical datasets: the Catastici and the Sommarioni. By comparing these records, it aims to uncover patterns in property ownership, tenancy, and rent payments among widows, shedding light on their economic mobility and societal roles.
The analysis is guided by several key questions. First, it seeks to identify and contextualize the widows recorded in both datasets, gathering demographic and economic details such as names, property statuses, and rent information. From this foundation, the study explores whether widows were more likely to be property owners (landlords) or tenants, offering insights into their relative economic standing.
Another critical focus is the comparison of rent dynamics. The project investigates whether widows paid different rents compared to other tenants for similar properties, exploring potential evidence of preferential treatment or discrimination. Additionally, by comparing widows’ ownership or tenancy statuses across the two datasets, the study examines changes in their economic positions over time—did widows acquire more properties or experience economic decline? Finally,... what do we do at the end, how do we conclude??
Through this multi-faceted approach, the project aims to contribute to a deeper understanding of widows’ socio-economic roles and property dynamics, offering a nuanced perspective on gender, property, and economic mobility in historical contexts.
(example for introduction from chat - need to double check that it coincides with project and that it doesnt include things we didnt do)
Historical backdrop
Motivation
Project Plan and Milestones
The project is structured on a weekly basis, to ensure an even progression and workload. Each week has a clearly defined goal. The plan spans from the initial setup and data extraction through to final analysis and presentation, with clear milestones throughout.
The first phase of the project (07.10 - 13.10) is focused on defining the project's scope and structure. Here the focus was on creating a common understanding of the project to ensure good collaboration in the group. The following week data extraction of the widows in the two datasets started. In addition a review of historical papers on widows and Venice was done, providing the necessary context for the research (14.10 - 20.10). The analysis then shifted towards examining the widows mentioned in the Sommarioni and Catastici records. This stage involved comparative rent analysis and property ownership evaluation (8.10 - 03.11).
The mid-project milestones included a midterm presentation on 14.11, with further development of the analysis through the end of November (11.11 - 24.11). This phase focused on completing the property ownership and comparative rent analyses, as well as beginning to explore widow heritage and social aspects, such as the frequency of titles like "Vedova" and "Consorte" used in the records. These findings were progressively written into a shared wiki.
The final analysis phase, beginning 02.12, was dedicated to comparing the results of the previously conducted analyses, and identifying overarching trends related to widows in Venetian society. The last steps of the project (09.12 - 15.12) will involve finishing the wiki documentation and preparing the final presentation.
The project will conclude with the delivery of the GitHub repository and wiki on 18.12, followed by the final presentation on 19.12.
For a detailed overview of the workflow and corresponding milestones, see the table below.
| Week | Task |
|---|---|
| 07.10 - 13.10 | Define project and structure work |
| 14.10 - 20.10 |
Write code to extract widow data |
| 21.10 - 27.10 | Autumn vacation |
| 28.10 - 03.11 |
Comparative rent analysis (catastici) |
| 04.11 - 10.11 |
Analysis: |
| 11.11 - 17.11 |
Midterm presentation on 14.11 |
| 18.11 - 24.11 |
Finish property ownership analysis - Sommarioni & Catastici |
| 25.11 - 01.12 |
Start widow heritage analysis |
| 02.12 - 08.12 |
Compare all analyses to identify general trends for widows |
| 09.12 - 15.12 |
Finish writing the wiki |
| 16.12 - 22.12 |
Deliver GitHub + wiki on 18.12 |
Dataset presentation
For this project the following two datasets will be used as a basis for conducting research.
Sommarioni [3]
Catastici
The Catastici is a register containing in total 32.123 records. Data for this register was collected walking door to door in a parish. By looking at the order of the transcribed data one can see which path was walked during the collection. The original Catastici contains the following five columns:
- Owner information
- Tenants
- Income from rent
- Place name
- Urban function
The entries in the Catastici were not written on a strict format, meaning the information given varies and can be very detailed but also lacking for some entries. Through standardisation of the data, additional columns where created to store information. These are for instance family name and owner title.
For the analysis the version "catastici_text_data_20240924.json" containing the transcription of the Catastici was mainly used. This set contains the original columns as well as the additional ones after standardisation.
Sommarioni
The Sommarioni is a cadaster from 1808 showing the different properties in Venice, parcels, and their assigned parcel number. The information is given in a tabular form. Information includes:
- Parcel number, relates to a certain property
- Owner of the given property
- Quality, describing the function of the property
As with the Catastici, multiple columns have been added after digitalisation and standardisation of the cadaster to better store all the information. The Sommarioni does not contain any information on the tenants of properties being rented.
Methodology
Property ownership analysis
For the porperty ownership analysis for the widows mentioned in the Catastici and Sommarioni a similar approach was used. First the widows where located using the keyword "vedova", meaning widow, and "consorte", meaning wife of dead husband. After filtering the datasets using row-wise text matching for these keywords, the entries of the widows where saved. These new data sets where then used as the basis of further analysis.
How specific should we be here? for every analysis give the exact mehtod or no
Heritage analysis
To explore inheritance patterns of widow-owned properties in Venetian records, two approaches where used:
Linking Catastici to Sommarioni Properties owned by widows in the Catastici were linked to entries in the Sommarioni through two primary methods:
- id_napo Matching: Directly relating id_napo (parcel numbers) from the Catastici to corresponding entries in the Sommarioni.
- Geometric Matching: Comparing spatial data where id_napo values were unavailable. This method was not applied in this project due to lack of time. But one could use the coordinates given in the Catastici and link it to parcels in the Sommarioni using the geojson.
Due to the limited amount of data avialable, only 16 entries with an id_napo in the Catastici, manual inspection was conducted to identify familial or functional connections.
Linking Sommarioni to Catastici Properties listed in the Sommarioni were traced back to the Catastici using parcel numbers and name similarity.
Using the parcel numbers from the Sommarioni, they were linked with the id_napo of the Catastici. To check for familiar relations between the owners a name similarity analysis was conducted. Here computational tools like difflib were used to compare widow names between datasets, accounting for spelling variations (e.g., "Bonvicini" vs. "Bonbicini"). A similarity threshold of 0.7 was applied.
This methodology allowed for a combination of qualitative and quantitative analysis, addressing historical inconsistencies while exploring inheritance patterns across records.
Results
Catastici property analysis
Sommarioni property analysis
Using the methods described in #Property ownership analysis, the study identified 659 entries related to widows out of a total of 23,400 entries in the Sommarioni. Since this dataset includes only property owners and excludes tenants, no conclusions can be drawn about the number of widows renting properties. Similarly, due to some widows owning multiple properties, it is impossible to determine the total number of widows living in Venice during this period.
When looking at how much property one widow holds, its important to ensure that it's the same widow. When comparing the data it appears that in the 'owner' category there are 443 unique owners, whilst in the 'owner_standardised' there are only 360 unique widows. This means that there must be some typos and errors in the way the widows are written in the 'owner' section compared to the cleaned and standardised section, which is as expected. When looking at the new list of widows, it is still possible to see the same widows, but written differently and further refinement is therefor necessary. After looking for similarities in the names, there are around 246 unique widows.
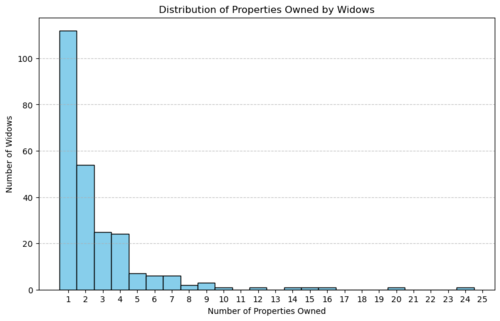
Most widows own a single property, as illustrated in the histogram below, which shows an exponential decrease in ownership frequency with increasing property counts.
From the data:
- The majority of widows own one property.
- The graph shows similarities to an exponential decay.
- The maximum observed ownership is 25 properties, held by Loredana Grimani, wife of Giovanni Morosini.
Loredana Grimani Loredana Grimani is the widows holding the most properties in Venice in 1808. This exceptional case may indicate significant wealth, and further investigation into the Grimani-Morosini family could provide more context. From the presentation given on the different datasets <ref> (FDH2024-1-7-VeniceData), there is a graph from showing the distribution of family ownership - weighted by ownership portion. This graph is based on data from the Catastici, but it is clear by looking at it that both the Morosini family as well as the Grimani family hold a big portion of the properties in Venice during this time.
The following graph compares the proportion of properties owned by widows to those owned by the general population in each district:
This comparison reveals significant regional differences:
- In Cannaregio, widows own a disproportionately large share of properties compared to the general population.
- In Castello, widow property ownership is notably lower than that of the general population.
- In Dorsoduro, San Marco, and San Paolo, widows own slightly more properties than average, while in Santa Croce, widows own slightly fewer properties.
These findings suggest that socio-economic and demographic factors may influence the distribution of widow property ownership across districts.
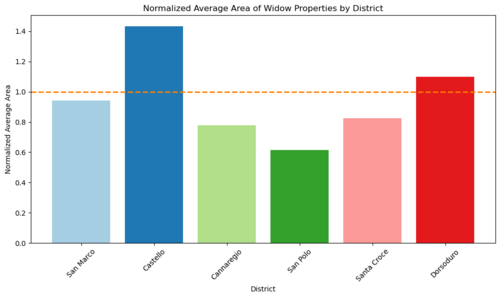
The graph below shows the normalized average area of properties owned by widows in each district, compared to the average property size in that district:
The graph below shows what the average area of a property owned by a widows in a given district is, normalized by the average area of the properties in that district. This might give an indication of the wealth of the different districts. Though it has to be said, that the area given in the Sommarioni is likely computed from the vectorization available in the GeoJSON file.
Key observations include:
- In Castello, widow-owned properties are approximately 40% larger than the average, a notable finding considering the low number of widows holding property there. This discrepancy may reflect wealth concentration among widows in Castello.
- In Dorsoduro, the average property size for widows is comparable to the district average.
- In other districts, widow-owned properties are generally smaller than the average, suggesting a relatively worse economic situation for widows in these areas.
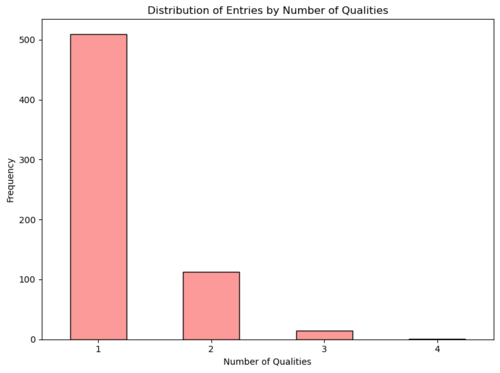
The final aspect of the analysis focuses on the types and functions of widow-owned properties. The graph below shows the distribution of properties by the number of distinct functions they serve:
From this data:
- Most properties serve a single function, while over 100 properties serve two functions.
- A smaller number of properties have three or four functions, which may reflect detailed notations in the Sommarioni or unique uses of these properties.
- Of the 659 widow-owned properties, 555 are rented (partially or fully), while 104 are not rented at all. The non-rented properties primarily include vegetable gardens (orto) and covered walkways (sottoportico).
- Only nine widows are listed as living in the properties they own, an unexpectedly low number that may merit further investigation.
Properties anlysis comparison
When comparing the results of the different analysis of the Catastici and Sommarioni only the intersection of the columns from the two sets are possible to use. This is due to the datasets not containing entirely the same data. An example for something that falls outside this scope is aspect of the tenants, due to them not being mentioned in the Sommarioni.
aspects to compare:
- amount of widows found
- distribution of districts
- function of buildings
Heritage analysis
The inheritance of property by widows in Venice offers insight into historical family dynamics and property ownership structures. This study examines links between property records in the Catastici and Sommarioni to identify patterns of inheritance. The analysis focuses on widows who owned property, as tenants are not mentioned in the Sommarioni.
Catastici to Sommarioni
Of the 61 widow-owned properties in the Catastici, only 16 contained valid id_napo values, enabling direct comparison. Manual inspection of these entries yielded the following results.
For seven of the entries there was no apparent relationship between the widow-owned properties in the Catastici and corresponding entries in the Sommarioni. For example, the property linked to id_napo 4270 (Catastici: Gerolema; Sommarioni: DA' RIVA Giovanni Battista) showed no familial or functional connection.
For another seven of the entries there is a possible relationship between the two datasets. Several cases suggested familial inheritance, often indicated by shared last names between the Catastici and Sommarioni entries. An example of this is id_napo 4896, where in the Catastici the owner of a house with a shop is called Elena Vianol (widow of Ferigo Renier). In the Sommarioni the owner is called Renier Bernardino, which is likely a family member.
Other recurring patterns seen in this analysis is that Elena Vianol (widow of Ferigo Renier) appeared in multiple instances where properties were inherited by individuals with the surname Renier. Paolina Mocenigo (widow of Michiel Morosini) showed a similar trend, with properties inherited by Morosini Elisabetta.
For some properties, the presence of both the widow's and her husband's names in different entries suggests a time lag in documentation, with the husband potentially recorded before his death and the widow afterward.
Sommarioni to Catastici
When attempting to trace properties from the Sommarioni back to the Catastici, 388 potential links were identified based on matching parcel numbers. Due to the large number of matches, computational methods were employed to identify connections.
The general idea would be to look if there is a similarity in their names. A problem here is that the names are sometimes written differently ( ex. Bonvicini and Bonbicini) even though its the same familyname.
The analysis revealed clear inheritance patterns in several cases, particularly among prominent families like the Renier and Morosini. These findings suggest that property often stayed within family lines, with widows playing a transitional role in ownership. However, discrepancies in documentation and name variation posed challenges, underscoring the need for refined computational methods and historical context in future studies.
Rent Analysis
What is the economical situation of widows in Venice in 1740 ?
When looking the entire city of Venice, we find only 120 properties involving widows from a total of more than 30k. This is about 0.36% of properties. We could expect this number to be closer to 15%. We are identifying the widows with keywords (consorte and vedova), so it is possible that some widows are mentioned with their name only, making them indistinguishable from unmarried women. Also, note that we cannot identify widows living at home or at a relative's place if they are not renting from them.
Most widows are probably able to own a house but not to have tenants, or they remarry, or they move to live with family members. This would explain why they don't appear in the Catastici. Also, widows in the Catastici are always either tenants or owners of a place.
We can therefore assume that there is three categories of widows :
- poor widows who have no choice but to rent a place
- supported widows who either own a home or have family support
- rich widows who own a property and are able to rent it
We will focus on the first and last categories, as we have no information about the middle one.
Charity
Not everyone is paying rent with money, or even paying rent at all. People can pay rent with money or goods (like sugar). However, no Widow owners was found receiving payment in goods and no widow tenants was found paying in goods. Properties with no rent paid (no good and no money) fall into three categories :
- charity, (for instance : "gratis": free , "per carità": per charity, "per grazia": per grace, "amore dei": for the love of God)
- refusal to pay, ("giurò non pagar affitto": swore not to pay rent)
- no comment
It is difficult to determine if no comment entries are mistakes and rent was actually paid or if they fall into charity or some sort of agreement between owner and tenants. But, if we only focus on entries for which we are sure that they are charity, it is clear that charity towards widow tenants is almost 7 times higher than charity in general. Widow owners were not found practicing charity, but remember that charity is rare and there is not a lot of widow owners, so this might not be a significant result.
| Total number of properties | Properties where no rent is paid (no good and no money) | Mentioned as charity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Venice | 33,297 (100%) | 3,115 (9.35%) | 169 (0.50%) |
| Widow Owners | 61 (100%) | 10 (16.39%) | 0 (0%) |
| Widow Tenants | 59 (100%) | 4 (6.78%) | 2 (3.39%) |
The scale of Venice
If we now only consider properties for which we have quantifiable rents paid with money, we find that widows pay about 40 lirae less than median rent per property and when owning a place, they earn about 40 lirae more than median rent per property. Those difference represent a 30% difference to median rent.
A possible explanation for widows renting at lower price would be that they get discounts due to their social status. But, this type of positive discrimination towards widows wouldn't explain why widows own properties that are rented at a higher price. Considering the previous observation that charity is rare, this phenomena might be a consequence of our hypothesis : poor tenat widows live in small, cheap places while rich widow owners possess big, expensive houses.
But this asks further questions: Are those properties located in specific cheap or expensive neighborhoods ? Where are widows renting ? Where do they own properties ? And are we sure that what we observe at the macro level of the city still holds at more micro levels ?
| Median Rent | Widow Owners Median Rent Difference | Widow Tenants Median Rent Difference | Properties | Widow Owned Properties | Widow Rented Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 124.0 | + 37.2 | - 37.2 | 29999 | 48 | 55 |
The scale of the districts
If we zoom in to the scale of districts, we can see that despite the high variations in rent between districts, the pattern of owners owning more than median rent and tenants renting at lower prices holds in almost every district.
We also see that widows are not present in equal proportions in each district. In particular, the Ghetto is very dense with both widow owners and widow tenants.
Widow tenants are present in good proportions in the Ghetto and Santa Croce, Cannaregio. Widow owners are present in good proportions at The Ghetto and a bit in Castello.
| Sestiere | Median Rent | Widow Owners Median Rent Difference | Widow Tenants Median Rent Difference | Properties | Widow Owned Properties | Widow Rented Properties Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Marco | 210.8 | + 37.2 | 0.0 | 5697 | 5 (0.09%) | 4 (0.07%) |
| Castello | 124.0 | + 99.2 | - 43.4 | 5774 | 14 (0.24%) | 8 (0.14%) |
| Cannaregio | 124.0 | + 55.8 | - 6.2 | 6016 | 6 (0.10%) | 20 (0.33%) |
| San Polo | 142.6 | + 24.8 | - 43.4 | 2930 | 3 (0.10%) | 3 (0.10%) |
| Santa Croce | 111.6 | - 12.4 | - 37.2 | 3218 | 5 (0.15%) | 10 (0.30%) |
| Dorsoduro | 86.8 | + 40.3 | - 24.8 | 5835 | 4 (0.07%) | 5 (0.08%) |
| Ghetto Novossimo | 124.0 | + 24.8 | - 62.0 | 529 | 11 ( 2.08%) | 5 (0.94%) |
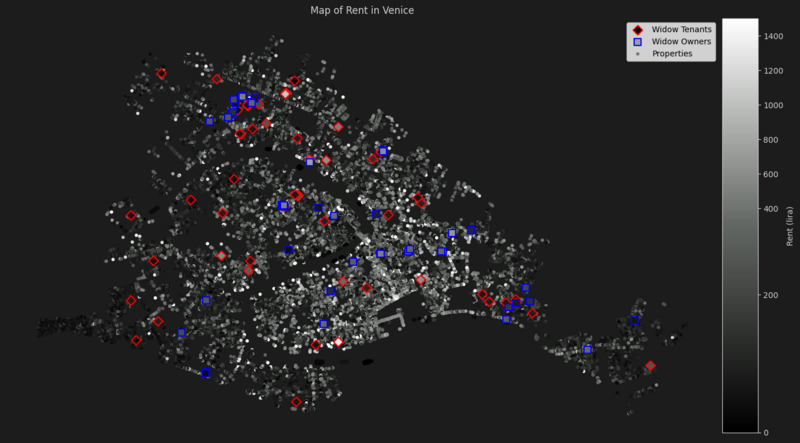
Let's look in detail at each district. For each of them, we can identify the parishes in which widows are involved. Parishes represent local religious communities, but people don't always belong to the parish closest to where they live. In the following plots, parishes are represented by a line encircling all of it's members. Sometimes, non members happen to fall inside the parish's shape despite not belonging to it. To be able to visualize this case, properties not belonging to the widows parishes are shown with a smaller diameter.
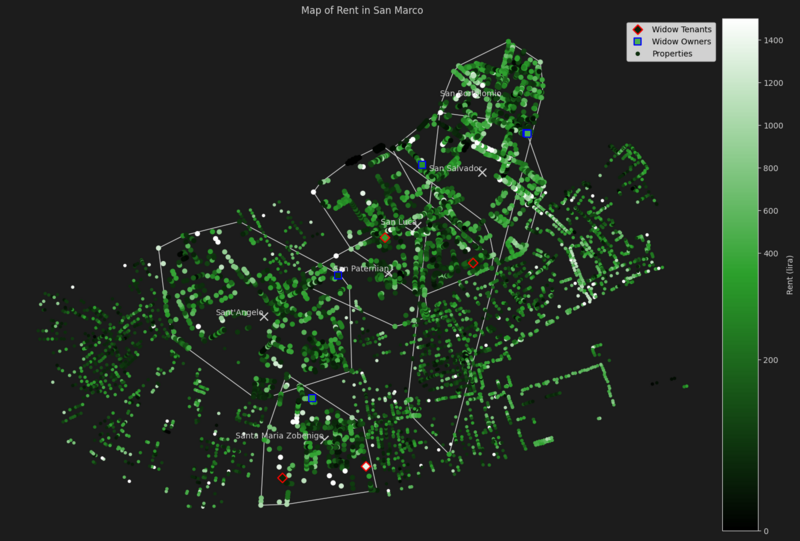
San Marco
San Marco is a very rich district where rent is almost double as in the rest of Venice. The widows representation in this district is quite low (less than 0.1%). Ignoring widows, the pattern of rents really highlights key commercial elements of the district. For instance the "Merceria" (the main shopping street in the parish of San Salvador) is really visible, because rent is very high on it.
| Parish | Median Rent | Widow Owners Rent Median Difference | Widow Tenants Rent Median Difference | Properties | Widow Owned Properties | Widow Rented Properties Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Bortolomio | 223.2 | + 24.8 | - | 503 | 2 | 0 |
| San Luca | 161.2 | - | -49.6 | 503 | 0 | 1 |
| San Paternian | 186.0 | - | + 124.0 | 178 | 0 | 1 |
| San Salvador | 272.8 | 5.2 | - | 521 | 1 | 0 |
| Sant'Angelo | 186.0 | -62.0 | - | 506 | 1 | 0 |
| Santa Maria Zobenigo | 183.4 | + 126.6 | + 529.6 | 256 | 1 | 2 |
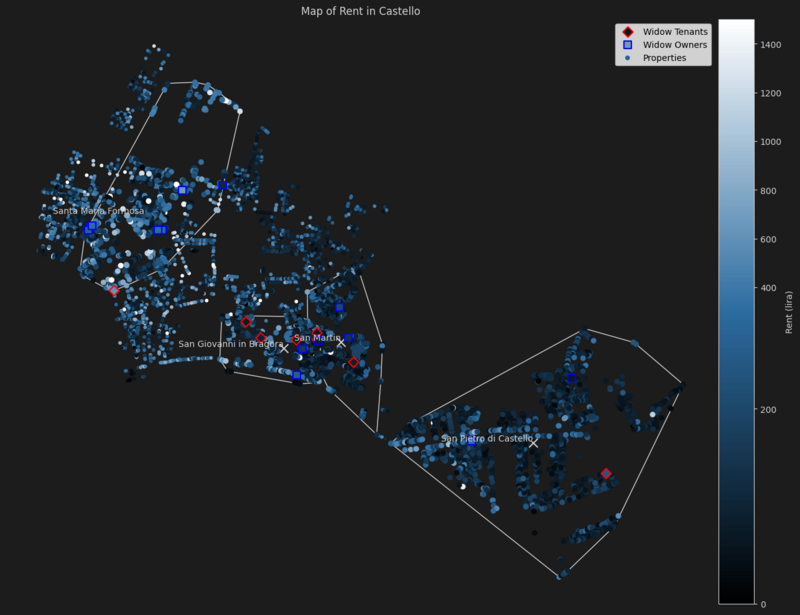
Castello
Castello has some widows, particularly owners, that really gather in specific parishes in the east of the district, in San Giovanni in Bragora, San Martin and Santa Maria Formosa.
| Parish | Median Rent | Widow Owners Rent Median Difference | Widow Tenants Rent Median Difference | Properties | Widow Owned Properties | Widow Rented Properties Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Giovanni in Bragora | 124.0 | + 84.3 | -52.7 | 399 | 2 | 4 |
| San Martin | 86.8 | + 49.6 | -6.2 | 563 | 3 | 2 |
| San Pietro di Castello | 99.2 | + 86.8 | + 142.6 | 1495 | 2 | 1 |
| Santa Maria Formosa | 186.0 | + 62.0 | + 434.0 | 747 | 7 | 1 |
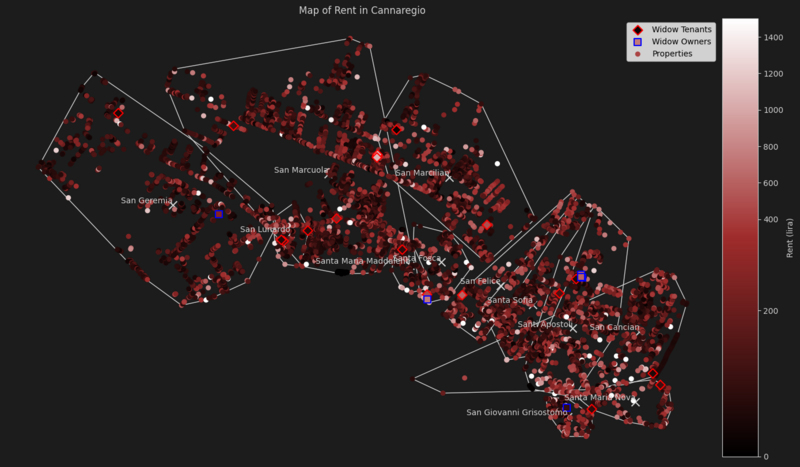
Cannaregio
Unlike in Castello, widows of Cannaregio are present in almost every parish. Tenants are better represented in Cannaregio.
| Parish | Median Rent | Widow Owners Rent Median Difference | Widow Tenants Rent Median Difference | Properties | Widow Owned Properties | Widow Rented Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Cancian | 124.0 | - | -62.0 | 629 | 0 | 1 |
| San Felice | 186.0 | - | + 434.0 | 351 | 0 | 1 |
| San Geremia | 99.2 | + 148.8 | -49.6 | 1082 | 1 | 1 |
| San Giovanni Grisostomo | 186.0 | -86.8 | - | 187 | 1 | 0 |
| San Lunardo | 148.8 | - | -74.4 | 117 | 0 | 3 |
| San Marcilian | 124.0 | - | + 136.4 | 589 | 0 | 2 |
| San Marcuola | 117.8 | - | + 83.7 | 1432 | 0 | 6 |
| Santa Fosca | 124.0 | + 620.0 | + 347.2 | 163 | 1 | 1 |
| Santa Maria Maddalena | 124.0 | - | -37.2 | 119 | 0 | 1 |
| Santa Maria Nova | 198.4 | - | -99.2 | 183 | 0 | 2 |
| Santa Sofia | 136.4 | - | 0.0 | 546 | 0 | 1 |
| Santi Apostoli | 161.2 | -49.6 | -99.2 | 618 | 3 | 1 |
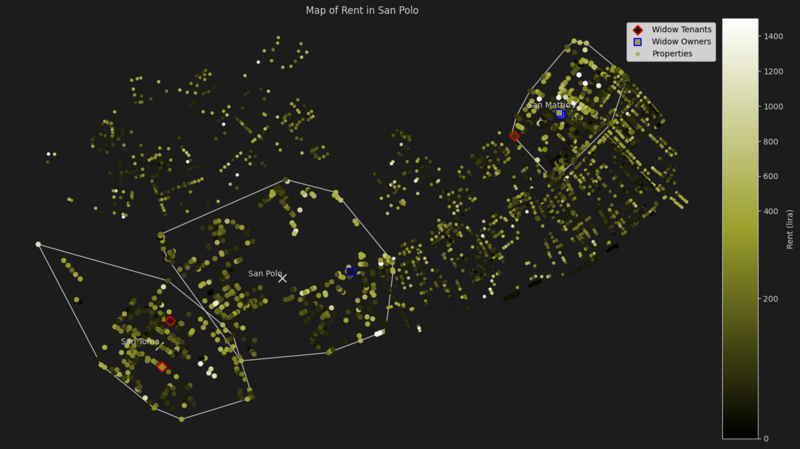
San Polo
Similarly to San Marco, widows are not very present in this San Polo.
| Parish | Median Rent | Widow Owners Rent Median Difference | Widow Tenants Rent Median Difference | Properties | Widow Owned Properties | Widow Rented Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Mattio | 136.4 | + 31.0 | -37.2 | 319 | 2 | 1 |
| San Polo | 161.2 | -117.8 | - | 353 | 1 | 0 |
| San Toma | 136.4 | - | + 24.8 | 272 | 0 | 2 |
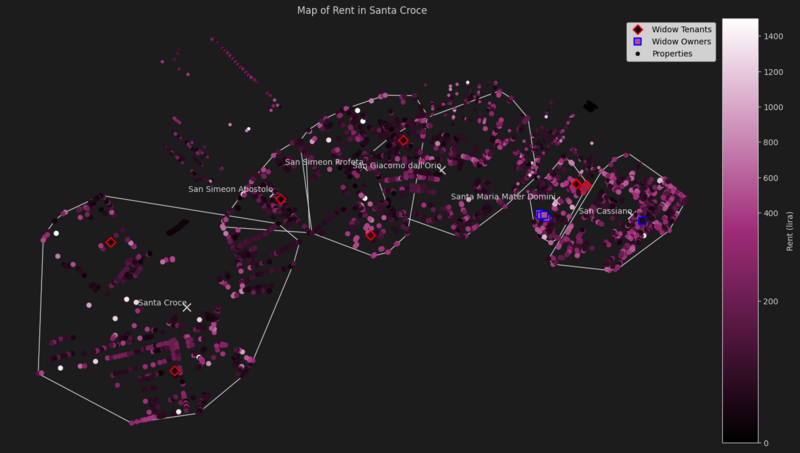
Santa Croce
| Parish | Median Rent | Widow Owners Rent Median Difference | Widow Tenants Rent Median Difference | Properties | Widow Owned Properties | Widow Rented Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Cassiano | 186.0 | -124.0 | - | 546 | 1 | 0 |
| San Giacomo dall'Orio | 99.2 | - | -55.8 | 657 | 0 | 1 |
| San Simeon Apostolo | 99.2 | - | -62.0 | 198 | 0 | 1 |
| San Simeon Profeta | 93.0 | - | 0.0 | 447 | 0 | 1 |
| Santa Croce | 111.6 | - | -58.9 | 739 | 0 | 2 |
| Santa Maria Mater Domini | 124.0 | + 3.1 | -31.0 | 152 | 4 | 5 |
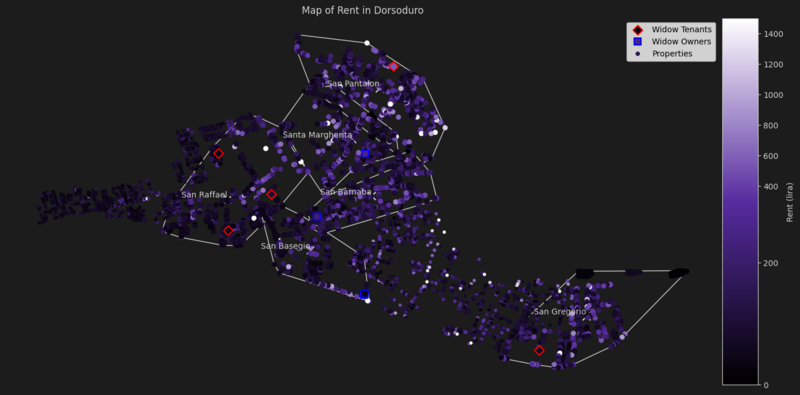
Dorsoduro
| Parish | Median Rent | Widow Owners Rent Median Difference | Widow Tenants Rent Median Difference | Properties | Widow Owned Properties | Widow Rented Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Raffael | 74.4 | - | -43.4 | 772 | 0 | 3 |
| San Barnaba | 124.0 | + 93.0 | - | 904 | 1 | 0 |
| San Basegio | 74.4 | -37.2 | - | 359 | 2 | 0 |
| San Gregorio | 86.8 | - | -24.8 | 487 | 0 | 1 |
| San Pantalon | 111.6 | - | + 446.4 | 639 | 0 | 1 |
| Santa Margherita | 99.2 | + 148.8 | - | 483 | 1 | 0 |
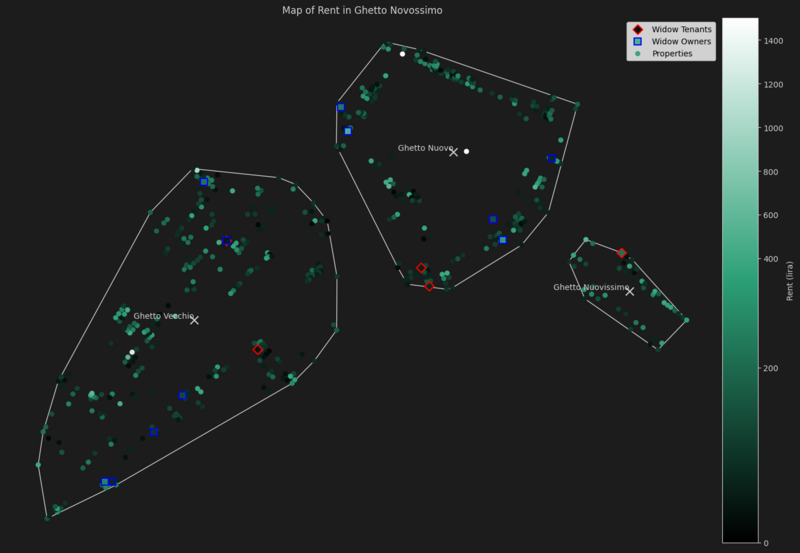
The Ghetto
| Parish | Median Rent | Widow Owners Rent Median Difference | Widow Tenants Rent Median Difference | Properties | Widow Owned Properties | Widow Rented Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ghetto Nuovissimo | 148.8 | - | + 68.2 | 46 | 0 | 1 |
| Ghetto Nuovo | 124.0 | + 105.4 | -55.8 | 207 | 5 | 2 |
| Ghetto Vecchio | 124.0 | -6.2 | -80.6 | 276 | 6 | 2 |
Discussion, limitations and quality assessments
should we maybe summarize, since we probably have similar limitations?
Lets make a list first:
Limitations
Methodological Limitations: Were there constraints in your methodology?
- Data: when looking at the heritage between the Catastici and the Sommarioni only 16 cases were identified using id_napo. This is too few to be able to say anything concrete about all widows.
- Not all columns have values, for instance for the heritage only 16 out of 61 entries had a id_napo.
- Tools: using difflib and searching for similarities in names
Data Limitations: Issues with data quality, availability, or representativeness.
- The standardised sections, like "owner_standardised" in the Sommarioni is not fully standardised. Still some different spellings of names or additional characters.
External Validity: Can your findings be generalized to other settings or populations?
- Sommarioni no tenants so cant really say anything about them. Also maybe the poorest widows not properly represented
Quality assessment
- Data Quality: Comment on the quality, completeness, and reliability of your data.: might be errors from person writign cadaster, but also through digitization, maybe the data also wrongly represents the reality of the situation for widows? But mention that it is mostly good
- Methodological Rigor: Methods might overlook some data, maybe too narrow
- Transparency and Reproducibility: Every analysis can be found in the GitHub
and also maybe all of this should be one coherent text and not discussion, limitations and qa each on its own
Conclusion and continuation
Conclusion
Continuation
This project has been an attempt to collect knowledge on the widows living in Venetian society between 1740 and 1808. There is still plenty to uncover about how life was for them and possible research areas are described followingly.
- look at the Tassini (explain what the Tassini is) and see if and how they mention widows
- try to do more on archetypes, maybe some qualitative analysis of familis
Deliverables
The main deliverables of the project is the results of the different analysis conducted during the span of the project and the tools used to extract the different data.
- should we go into more detail on what is to be found in the git?
- maybe mention which tools can be reused when conducting further analysis
- maybe talk again about resutls
Credits
Course: Foundation of Digital Humanities (DH-405), EPFL
Professor: Frédéric Kaplan
Supervisor:
Authors: Eglantine Vialaneix, Nathanaël Lambert, Lisa Marie Njå
Date: 18.12.2024
References
- if for instance the figures of the Catastici is taken from the PP from the lecture https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fo/tu5waw0623hcp4537lx6u/AKx-eznaH6BRddo1goaF7OE?dl=0&e=1&preview=FDH2024-1-7-VeniceData.pdf&rlkey=jiewdfpk5ysyv92m1817sk5qc&st=01697apo, do we need to reference to it?
should include references to the historical sources used for the historical background
- how do we want to reference to slides from the lecture?
Supplementary Information
| Italian | English | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vedova | widow | Refers to a woman whose husband has passed away. |
| mestiere | profession | A term used to describe one's occupation or trade. |
| parrocchia | parish | Parishes in Venice were local religious districts, each centered around a parish church. Every house in Venice belonged to a specific parish, forming a network of smaller communities within the larger city. |
| sestiere | district of Venice | The name given to the districts of Venice: San Marco, San Polo, Santa Croce, Dorsoduro (which includes the island of Giudecca), Castello, and Cannaregio. |
| fratelli | brothers | The plural form of 'fratello' (brother). |
| sorelle | sisters | The plural form of 'sorella' (sister). |
| ved | widow of | An abbreviation of 'vedova'. |
| quondam | son/daughter of | Literally means "formerly" or "previously." Often used in historical contexts to indicate lineage. |
| fratelli quondam | brothers of the father | Refers to a person and their brothers from the same father (e.g., siblings from a deceased patriarch). |
| fu di | of the late man | Similar to 'quondam', but explicitly indicates that the father is deceased. |
| q.m. | abbreviation of quondam | A shorthand version of 'quondam' used in records and documentation. |
| sudett-o/-a/-i | part of another place | Indicates that certain rows in a table belong to one geographical or administrative area. |
| consorte | married with | Indicates a spouse, often implying the husband is deceased. |
| della fu | of the late woman | Used to indicate lineage or connection to a deceased mother. |
For our eyes only
TODO (guideline):
-Motivation and description of the deliverables (5%) (>300 words) -Detailed description of the methods(5%) (>500 words) -Quality assessment and discussion of limitations (5%) (>300 words)
TASK SPILT: - everyone write down their own results, discussion and limitations (merge the common ones) - we later split the rest of common sections
TODO later:
- methodology
- introduction + historical backround and motivation ( maybe Nathanael can talk briefly about the historic context?)
- conclusion and continuation
- deliverables
Historical background
Where do we want to find this information? What are good sources to use? --> Google Scolar?
When reading about the history, add knowledge here with references to the sources used.
Venice is part of the Venetian Republic. It falls to Napoleon in 1796. Venice is given to the Austrian Monarchy by the French Republic as part of the Treaty of Campo Formio. Then it became French again and then Austrian.
https://www.napoleon-series.org/research/government/diplomatic/c_campoformio1.html
There is no major Palgue Epidemy during our period of focus [13]
The Venetian Society has strong gender roles and has a class system:
- Patricians (there names are probably in the libro d'Oro - Citizens (Popolani) - Commoners
I wish I had access to : [14]
this looks cool : [15]

![Sommarioni [3]](/images/thumb/6/6a/Sommarioni.png/348px-Sommarioni.png)